China beef ban limited impact
 Last week we wrote about how the increasing tariffs on US Beef entering Japan is expected to have a small positive impact on export beef, and cattle prices. Obviously the support hasn’t been strong enough to stop price falling, but is the China import ban causing the fall?
Last week we wrote about how the increasing tariffs on US Beef entering Japan is expected to have a small positive impact on export beef, and cattle prices. Obviously the support hasn’t been strong enough to stop price falling, but is the China import ban causing the fall?
The China import ban is limited to six export beef plants, in Queensland, New South Wales and South Australia. While the reason for the bans seem rather trivial, the impact on individual plant is likely to be relatively severe. The bans were apparently due to mislabelling, with labels inside boxes not matching labels on the outside of the box.
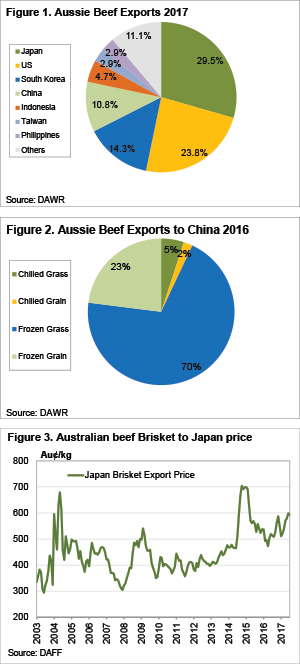
Regardless of the reason for the ban, any limitation of export to a particular market will result in weaker demand for beef, and stronger supply into other markets. Figure 1 shows that China is Australia’s fourth largest market for beef exports. It accounted for 10.8% of our exports for the first half of 2017.
If we take Australian domestic consumption into account, China receives 7.7% of Australian beef. There are currently 46 meatworks which can export beef to China, so there are still 40 works which can still send beef.
In terms of the type of beef, figure 2 shows that in 2016 a vast majority, 70% of Australian beef exported to China, was Frozen Grassfed; while Frozen Grain made up 23%. In terms of cuts, a wide variety is sent to China. According to MLA figures, ‘other’ was the largest category in 2016, accounting for 35% of exports. Brisket was the second largest category, making up 23% of Chinese exports.
As a comparison, in 2016 Australia sent 21,689 tonnes of Brisket to China. Japan took 42,381 tonnes of brisket in 2016, being the second largest cut exported there. Given the Japan tariff hike on US beef is likely to increase demand for Australian frozen briskets, there is likely to be some substitution from Chinese to Japanese markets.
Key points:
- The Chinese ban on six Australian meatworks is yet to be resolved.
- The proportion of Australian beef production impacted by the ban is relatively small.
- Chinese beef imports from Australia are largely made up of grassfed beef, any impact will be felt at this end.
What does this mean?
Given the amount of beef which is likely to impacted by the Chinese ban on six meatworks, the effect on price at saleyard level is unlikely to be noticeable. Figure 3 shows the price of Frozen Briskets exported to Japan, which hit a two and half year high in July. While there are plenty of other factors which come into play with export beef prices, this is the series most likely to show how export issues are impacting the market.
Other comments:
Include here any additional information or specific comments to ensure successful upload by the web manager